Bloodborne Pathogens Protection (BBP)

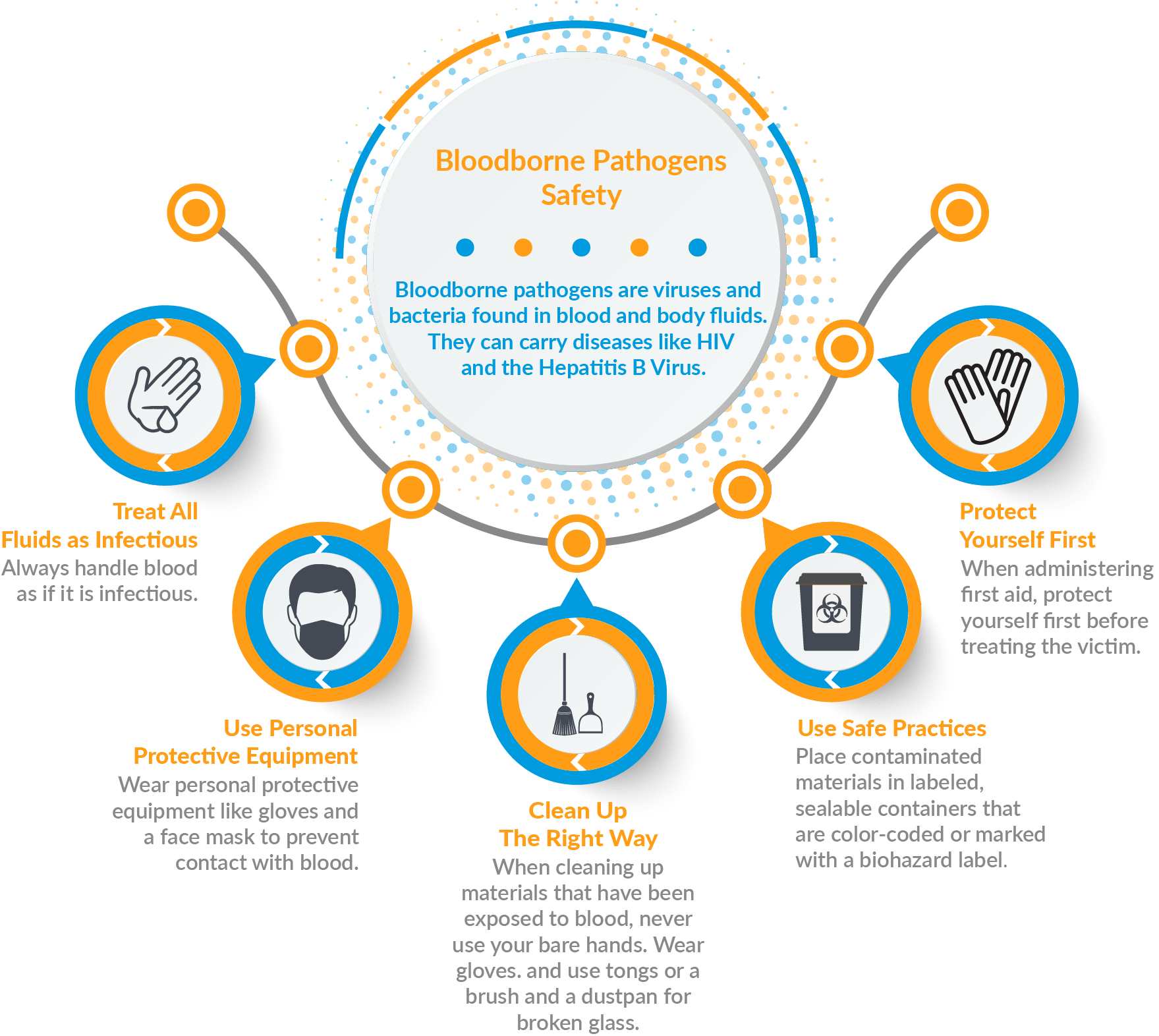
This safety training tip topic is bloodborne pathogens (BBP) are viruses and bacteria found in human blood or body fluids. BBP can cause diseases, most notably HIV and the Hepatitis B virus.
BBP training should include protective measures.
Here are some steps to help protect against exposure and contamination to bloodborne diseases:
1. Treat All Fluids as Infectious
The first rule in handling human blood and body fluids is to always handle it as if it is infectious. Even if you believe the fluid is disease-free, treating it as hazardous provides you with protection that you may be very thankful for later.
2. Use Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment, also known as PPE, is extremely important in preventing contact with blood. Common forms of PPE that decrease the likelihood of contracting a disease through blood and other body fluids are gloves, gowns, and face protection.
Latex gloves and vinyl aprons or gowns protect your skin from coming in contact with infectious fluids. Face protection, such as face shields and eye goggles, prevent blood from entering mucous membranes via the eyes, nose or mouth. latex-gloves-and-mask.jpg, medical-goggles.jpg
3. Protect Yourself First
When administering first aid, protect yourself first before treating the victim. Immediately put on the proper PPE for the situation. This may be hard when a co-worker is hurt, but you are putting your own health at risk when you don’t use protective equipment.
4. Clean Up the Right Way
Using protective measures when cleaning up after an accident is just as important as using PPE while treating the injury itself. When cleaning up broken glass that has been exposed to blood or body fluids, never use your hands, even if you are wearing gloves. Get rid of contaminated broken glass with tongs, or a brush and dust pan.
If you get blood or body fluids on you clothing, carefully turn the garment inside out as you remove it to prevent spreading the contaminants. After removing personal protective equipment and dirty clothing, wash all affected body parts to remove potentially infectious contamination.
5. Use Safe Disposal Practices
Get rid of materials that have come in contact with blood and body fluids. Handle all trash as if it contains sharps or infectious items. Place all potentially infectious materials and contaminated items in labeled, sealable containers. Make sure containers are color-coded or marked with a biohazard label.
We hope you gained a safety training skill today. Until next time, stay positive and stay safe.